Abstract
Introduction. Cell and gene therapy are emerging novel approaches for cancer treatment. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are non-hematopoietic progenitor cells, which can be isolated from different types of adult tissues. Due to their tropism to the tumor site, MSCs could be used to deliver various antitumor agents, including cytokines, which could prevent and delay metastases. Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is an immunomodulating cytokine, which regulates the activities of white blood cells. This cytokine is often used as immunomodulatory in cancer treatment. In this study we investigated whether expression of IL-2 in MSCs will affect the expression of key cancer-related genes.
Methods. Human MSCs were isolated from adipose tissue and transduced with recombinant lentiviruses encoding human IL-2 gene. The IL-2 expressing cells were selected using blasticidin S (5 μg/ml) for 10 days. The IL-2 gene expression was confirmed by quantitative PCR. The effect of the conditioned medium (CM) from native MSCs or MSC-IL2 on peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) activation was investigated. CM was harvested 72 hours after culture PBMCs in MSC-IL2 CM. CM from native MSCs or fresh DMEM/F12 were used as control. PBMC were collected and used for flow cytometry analysis.
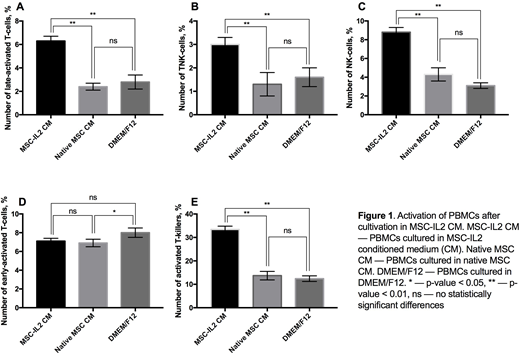
Results. We found that 6.3±0.4% of PBMCs cultured in the presence of MSC-IL2 CM were positive for CD3/HLA-DR, typical for late T-cell activation. The percentage of CD3/HLA-DR-positive PBMCs cultured in the presence of CM from native MSCs and DMEM/F12 medium was half as much, 2.4±0.3% and 2.8±0.6%, respectively (Fig. 1A).
We have shown that 3.0±0.3% of PBMCs cultured in the presence of CM from MSC-IL2 were positive for CD3/CD56 markers, typical for a population of TNK cells with both T-cell and NK-cell functions. The percentage of CD3/CD56-positive PBMCs cultured in the presence of CM from native MSCs and DMEM/F12 medium was 1.3±0.5% and 1.6±0.4%, respectively (Fig. 1B).
We observed an increased number of NK cells after culturing in the presence of MSC-IL2 CM with 8.8±0.5% of PBMCs were CD56-positive and CD3-negative. The percentage of CD56+/CD3- PBMCs cultured in the presence of CM from native MSCs and DMEM/F12 was about two fold less, 4.3±0.7% and 3.1±0.3% respectively (Fig. 1C).
Number of CD3+/CD25+ cells, characteristic of early activation of T-cell, was 7.1±0.3% when PBMCs were cultured in the presence of MSC-IL2 CM. The percentage of CD3/CD25-positive PBMCs cultured in the presence of CM from native MSCs and DMEM/F12 medium was higher, 6.9±0.4% and 8.0±0.5%, respectively (Fig. 1D). This could be explained by prolonged cultivation of the samples (72 hours).
Analysis of activated T-killer population, CD8+ and CD38+, revealed that 33.4±1.4% of PBMCs cultured in the presence of MSC-IL2 CM were CD8+/CD38+. The percentage of CD8+/CD38+ PBMCs cultured in the presence of CM from native MSCs and DMEM/F12 was about two fold less, 13.7±1.8% and 12.4±1.2%, respectively (Fig. 1E).
Conclusion. Conditioned medium from MSC expressing IL-2 increased number of key leukocyte populations, such as late-activated T-cells, NK cells, and activated T killers. The ability of IL-2 to activate cells of the immune system, as well as the natural tropism of MSCs to tumor sites, could make IL-2 expressing MSCs useful gene delivery tool for cancer immune therapy.
This study was supported by Russian Science Foundation grant 18-74-10044 and Program of Competitive Growth of KFU. RAA was supported by state assignment 20.5175.2017/6.7.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal